Looking at the Red Flags
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a condition where your body has a low number of platelets. Platelets help your blood clot, so with ITP, you may have problems with bleeding. It’s important to recognize the signs early so you can get treatment.
Signs of ITP
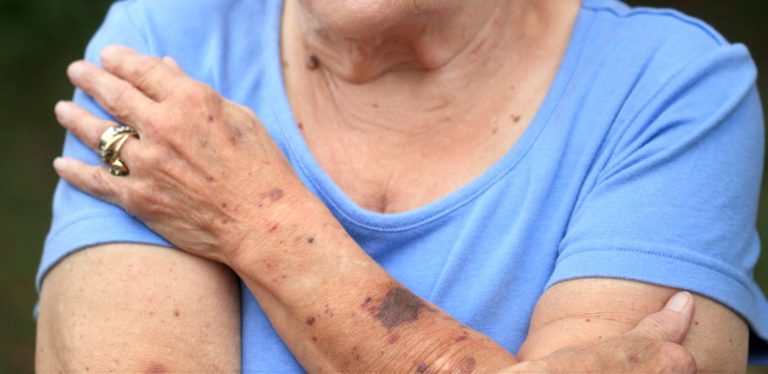
Easy Bruising
People with ITP may bruise easily. You might notice bruises even if you didn’t bump into anything hard.
Small Red or Purple Spots
Tiny red or purple spots, called petechiae, can appear on your skin. These spots happen when small blood vessels leak.
Frequent Nosebleeds
If you get nosebleeds often and they take a long time to stop, this could be a sign of ITP.
Bleeding Gums
Your gums might bleed when you brush your teeth or eat hard foods. The bleeding may be more than usual.
Heavy Menstrual Periods
Women with ITP may have periods that are heavier than normal or last longer than usual.
Blood in Urine or Stool
Sometimes, people with ITP may notice blood in their urine or stool. This can be a sign of internal bleeding.
Prolonged Bleeding from Cuts
If you get a cut, the bleeding may take longer to stop than usual. This happens because you don’t have enough platelets to help clot the blood.
Fatigue
Feeling very tired or weak is another sign of ITP. This can happen because your body is working harder to deal with the blood issues.
Bleeding Under the Skin
You might notice large areas of bleeding under the skin that look like dark bruises.
Headaches or Dizziness
In severe cases, people with ITP might have headaches or feel dizzy. This could be a sign of bleeding in the brain, which needs immediate attention.
Treatments for ITP
If you have ITP, treatment can help increase your platelet count and reduce the risk of bleeding. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Corticosteroids, like prednisone, are often used to raise your platelet levels. Other drugs, like immunoglobulins or rituximab, may also be used.
- Platelet transfusions: In some cases, doctors might give you a platelet transfusion to quickly increase your platelet count.
- Splenectomy: For some people, removing the spleen (splenectomy) can help. The spleen plays a role in breaking down platelets, so removing it can help increase platelet numbers.
- Thrombopoietin receptor agonists: These drugs help stimulate your body to make more platelets.
- Lifestyle changes: Your doctor may advise avoiding certain activities that increase your risk of bleeding, like contact sports.
Recognizing the Signs
Recognizing the signs of ITP early is important for getting the right treatment. If you notice unusual bruising, bleeding or any of the other symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor. With the right care, you can manage ITP and reduce the risk of complications.
Read on to learn about the common signs of celiac disease.